RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus): 7 Must-Know Factors for Success
RSV, or Respiratory Syncytial Virus, is a common respiratory virus that infects most children before their second birthday and can cause severe respiratory infections in older adults. If you are the parent of a baby or young child, it's essential to know how to recognize the symptoms of RSV and what treatment options are available for healthy children. In this blog post, we will provide you with a thorough understanding of RSV - from its definition and transmission to its symptoms and diagnosis. We'll also discuss the current treatments and prevention strategies for RSV as well as new treatments currently in clinical testing. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to recognize and treat RSV effectively.
Understanding RSV: A Brief Overview
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common viral illness that can affect people of all ages, but infants and young children are at high risk for severe respiratory illness, especially those with underlying health conditions like asthma. RSV is primarily spread through close contact with an infected person, and it can cause inflammation of the small airways in the lungs. Symptoms of RSV infection include cough, runny nose, and trouble breathing. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required, especially for children with underlying health conditions like lung disease or heart disease. Currently, there is no specific treatment for RSV, but supportive care such as IV fluids and oxygen therapy can help manage symptoms. Educational campaigns and the RSV vaccine have been developed to prevent RSV infections and reduce the severity of the illness. It is important for parents, especially new parents, to stay informed about RSV and its impact on children's health.
Defining RSV and Its Impact on Adults
RSV, or respiratory syncytial virus, is a common respiratory virus that can affect adults of all ages. Adults with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions are at higher risk of severe illness from RSV. Infection with RSV in adults can lead to complications such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis, which causes inflammation of the small airways in the lungs. It's important to recognize the symptoms of RSV in adults, including coughing, sneezing, and difficulty breathing. If you or someone you know is experiencing severe respiratory symptoms, seeking medical care is crucial.
RSV Transmission: Are Young Kids the Main Carriers?
Are young kids the primary carriers of RSV? While they can transmit the virus, it's important to note that adults can also spread RSV to others. The virus is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets, coughing, and sneezing. Practicing good hygiene, such as handwashing, and staying informed about CDC recommendations can help prevent RSV transmission.
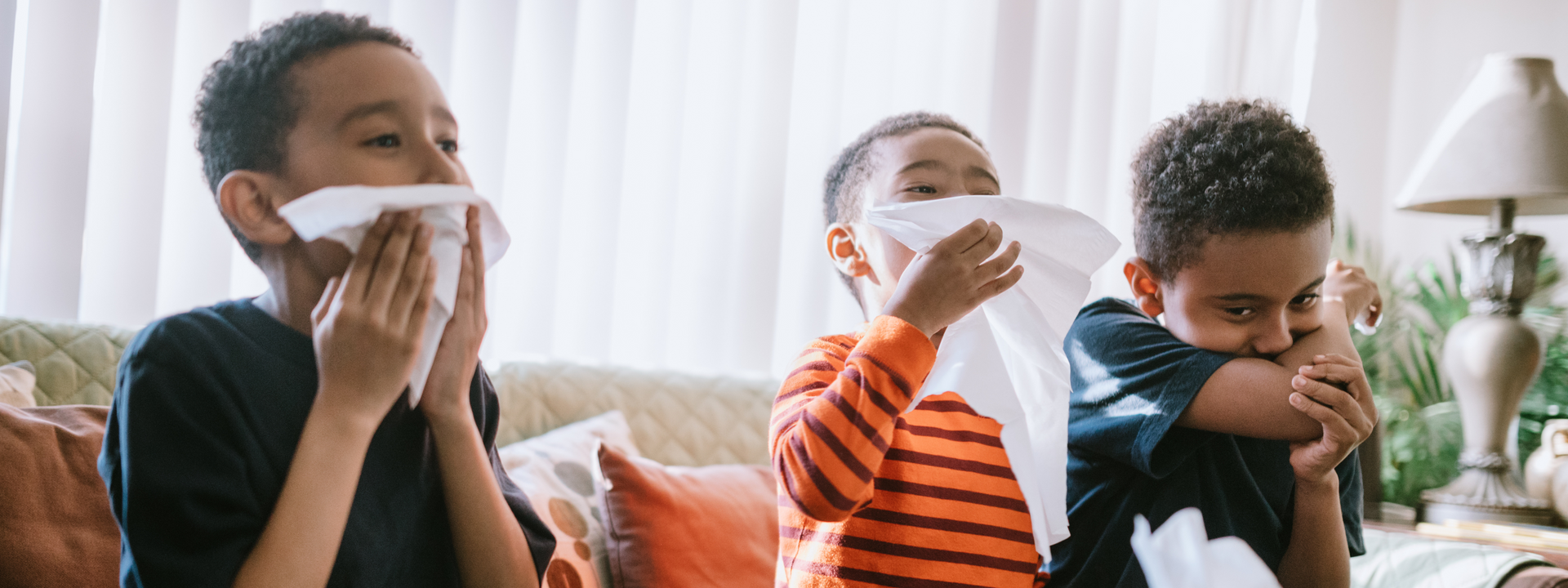

Recognizing RSV: Symptoms to Look Out For
To effectively recognize RSV, it's important to be aware of the common symptoms associated with this viral illness. These symptoms include a runny nose, cough, fever, and flu-like symptoms. It's crucial to understand the difference between mild RSV symptoms and severe illness or complications. Early detection and prompt medical evaluation are key in ensuring timely treatment for both children and adults. Additionally, it's important to note the similarities and differences in symptoms between RSV and COVID-19. Staying informed about the RSV season, which poses a higher risk of infection during certain months of the year, is vital.
Common RSV Symptoms in Adults
Adults infected with the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) may experience mild symptoms that are similar to those of a common cold, also known as cold symptoms. These symptoms include a runny nose, coughing, and sneezing. It is important for adults, especially those with underlying health conditions, to understand the potential complications of RSV and seek medical evaluation if their symptoms worsen or if they develop difficulty breathing. Treatment options for RSV in adults typically involve supportive care and antiviral medications. By staying informed about the recommended treatments, adults can better manage their symptoms and prevent further complications.
RSV vs COVID-19 Symptoms: How to Differentiate
Differentiating between the symptoms of RSV and COVID-19 is important to ensure appropriate care and management. While both respiratory illnesses share some common symptoms, there are key differences to be aware of. RSV is typically associated with symptoms such as a runny nose, cough, and fever. On the other hand, COVID-19 commonly presents with respiratory symptoms, loss of taste, and difficulty breathing. Diagnostic testing plays a crucial role in accurately differentiating between these two conditions. Those who start feeling symptoms of a respiratory illness and are unsure of whether they have RSV or COVID-19 are recommended to take an at-home COVID-19 test to help make differentiation easier.
RSV Diagnosis: What Does the Process Involve?
The diagnostic process for RSV involves various tests, such as viral swabs and rapid antigen tests, to identify the presence of the virus. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in evaluating respiratory symptoms and interpreting test results for a child’s symptoms. It is important to seek medical attention, especially for high-risk individuals, and be aware of the accessibility of diagnostic testing in healthcare settings.
Diagnostic Tests for RSV
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in identifying respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. One commonly used test is the viral swab test, specifically the RSV RT-PCR, which detects the presence of the virus. Rapid antigen tests are also available, providing quick results, but they may have lower sensitivity compared to viral swab tests. It's important to note that healthcare providers should evaluate and interpret test results for accurate diagnosis. Diagnostic testing for RSV can be accessed in various healthcare settings, clinics, and laboratories.
When Should You Contact a Healthcare Provider?
If symptoms of RSV worsen or breathing difficulty develops, seek medical care. Contact a healthcare provider if high fever, severe cough, or dehydration occurs, or if you experience any breathing problems. Evaluation by a healthcare provider is important, especially in high-risk individuals like young infants and older adults. Look out for signs of severe illness and seek immediate medical attention. Stay informed about the accessibility of healthcare facilities and emergency services for managing RSV symptoms.
Treating RSV: Available Options and Effectiveness
When it comes to treating respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), there are several options available. One of the main approaches is supportive care, which involves managing symptoms and providing comfort to the patient. Additionally, antiviral medications can be prescribed to reduce the severity and duration of RSV symptoms, especially in high-risk individuals. In severe cases, respiratory support like supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation may be necessary. It's important to stay updated with recommendations from healthcare authorities, as they may include the use of specific medications like palivizumab, given as monthly injections during the RSV season, for high-risk infants. Lastly, close monitoring and follow-up care are essential to address potential complications of RSV infection.
Current RSV Treatments and Their Success Rate
Current treatment options for RSV include supportive care, such as administering fluids and fever reducers. In severe cases of RSV infection, antiviral medications like ribavirin may be prescribed. Healthcare providers may recommend hospitalization for high-risk individuals, particularly infants with severe illness. The success rate of RSV treatments, including the use of antibiotics, varies depending on the severity of the infection and the overall health of the patient. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most effective treatment plan for RSV. Remember, seeking medical advice is essential, especially for high-risk individuals.
The Role of Vaccines in Preventing RSV
Currently, there is no vaccine available for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). However, ongoing research is focused on developing vaccines to combat RSV. These potential vaccines could play a crucial role in preventing severe RSV infection, especially among high-risk populations. Staying updated on the latest vaccine developments, or even participating in vaccine research as a volunteer, is important as it offers hope for future prevention strategies. In the absence of vaccines, taking preventive measures such as practicing good hand hygiene can help reduce the risk of RSV transmission.
Prevention Strategies for RSV
To prevent the spread of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), it is crucial to follow effective prevention strategies. One of the most important steps is to wash your hands frequently, especially before touching your face or doorknobs. Avoid close contact with sick individuals, particularly infants, young children, and older adults who are at high risk of severe illness from RSV. Remember to cover your nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing, either with a tissue or your elbow. Additionally, clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs to reduce the risk of RSV transmission. If you experience symptoms of respiratory illness, like a cough, runny nose, or fever, stay home to prevent spreading RSV to others.
How Often Can One Get RSV?
RSV infection can occur multiple times in a person's lifetime as the immune system's protection decreases over time. Severity tends to decrease with subsequent infections, especially in healthy individuals. Take preventive measures to reduce the risk of reinfection and protect high-risk individuals. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on RSV frequency in your situation.

The future of RSV Treatments
Ongoing research in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) focuses on developing new treatment options. Scientists are investigating the use of antiviral drugs that target the virus's replication process. Another promising avenue is monoclonal antibodies, which mimic the immune system's response and could be effective therapies for high-risk individuals. And there's hope for prevention too: advances in vaccine development may offer new strategies to combat severe RSV illness in the United States. Collaborative efforts among researchers, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical companies are driving progress in RSV treatment options. Excitingly, new RSV treatments are currently undergoing clinical testing.
New RSV Treatments In Clinical Testing
Several promising respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) treatments are currently in the process of being evaluated in clinical trials. Researchers are evaluating RNA-based therapeutics like small interfering RNA (siRNA) to determine their ability to inhibit viral replication. Additionally, novel antiviral compounds, including fusion inhibitors, are being studied for their effectiveness in preventing viral entry into cells. Another area of focus is immunomodulatory therapies, which aim to balance the immune response to RSV infection. These new treatments hold immense potential to improve outcomes, particularly in high-risk populations. The ongoing clinical testing signifies a significant advancement in RSV treatment options.
Overall, it is crucial to be aware of the impact RSV can have on both adults and young children. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely diagnosis and treatment is essential for a speedy recovery. While there are current treatments available, ongoing research and development offer hope for more effective options in the future. Additionally, preventive measures such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and considering vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of contracting RSV. Stay informed about the latest updates on RSV treatments and take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this respiratory infection. Remember, early intervention is key in managing RSV effectively.



