5 Signs You May Have a UTI
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections caused by the invasion of bacteria into the urinary tract system. This bacteria typically resides on the skin or rectum, but leads to infection when it enters the urethra. While both men and women can develop UTIs, women are more prone to them due to the shorter length of their urethra, which makes it easier for the bacteria to travel to the bladder.
It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of a UTI for early detection and appropriate treatment. While most urinary tract infections involve the infection of the lower urinary track -the bladder and the urethra -an unattended urinary tract infection that continues to spread to the kidneys can cause substantial health risk. Here, we'll go over the common signs and symptoms that indicate a urinary tract infection.
1. Frequent and/or Painful Urination
One of the hallmark symptoms of a UTI is a frequent urge to urinate, coupled with a burning or painful sensation during urination. This phenomenon, known as dysuria, occurs due to inflammation and irritation of the urinary tract caused by the infection. The urge to urinate may persist even when the bladder is empty, and the pain can be quite intense. For instance, a person may feel the need to urinate every few minutes but only produce a small amount of urine each time.
2. Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine
The presence of cloudy or turbid urine with a strong, unpleasant odor is a common indicator of a UTI. The cloudiness is a result of white blood cells, bacteria, or mucus being present in the urine due to the infection. This change in appearance and smell occurs because the infection disrupts the normal composition of urine. However, it is crucial to note that changes in urine color and odor can also be caused by other factors, such as certain medications or foods. Therefore, consulting a healthcare professional is vital to determine the underlying cause accurately.
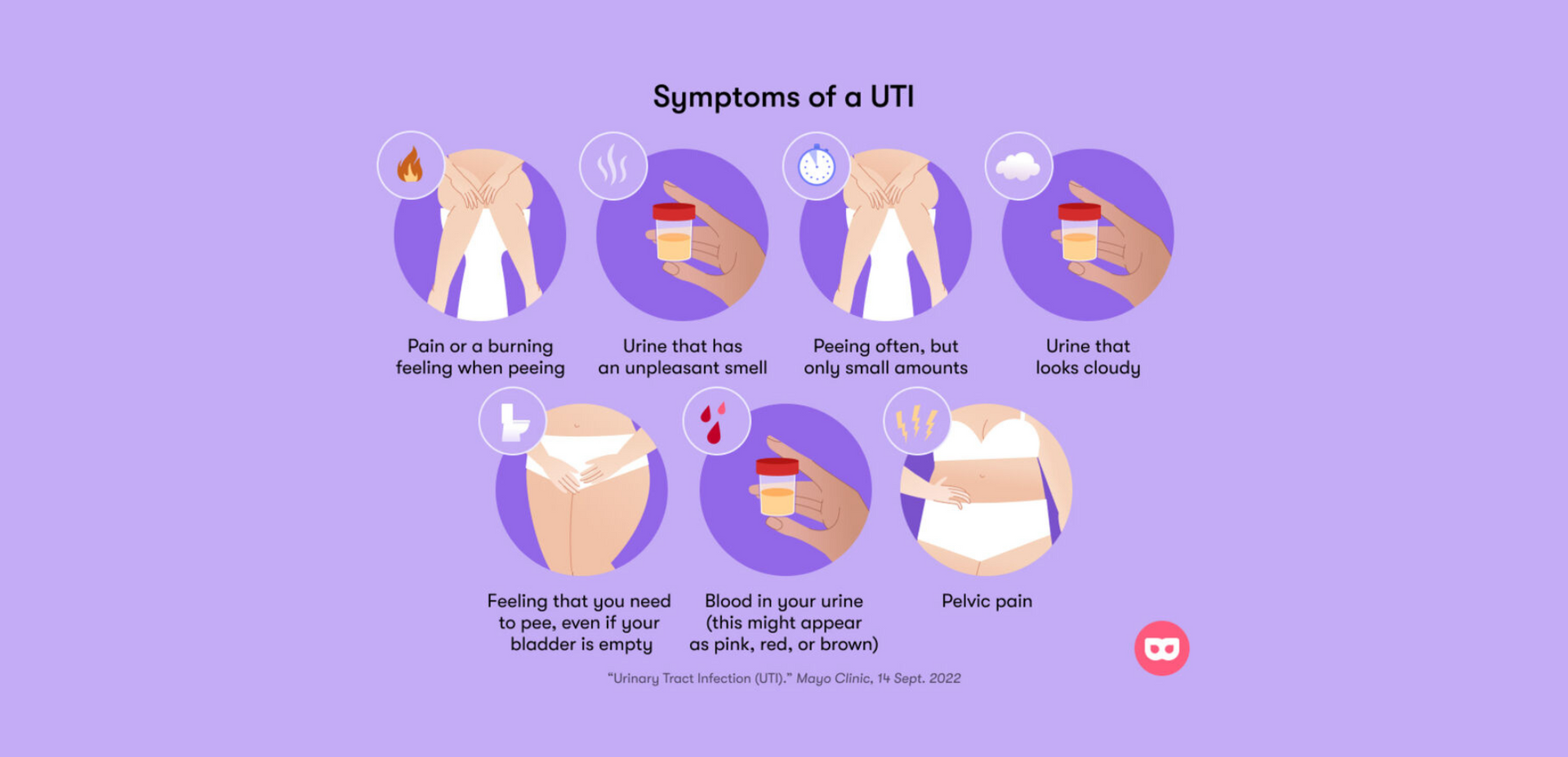
Photo by Flo
3. Lower Abdominal or Pelvic Pain
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain is a frequent symptom associated with UTIs. The infection-induced inflammation and irritation in the bladder/urethra can cause discomfort or pain in these regions. The severity of the pain can vary from mild to severe and may persist even after urination. For example, a person with a UTI may experience a constant dull ache or sharp, cramp-like pain in the lower abdomen.
4. Presence of Blood in the Urine
While not always present, a UTI can cause irritation and damage to the urinary tract, leading to bleeding. As a result, the color of the urine may appear pink, red, or brownish due to the presence of blood. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional immediately if you notice blood in your urine, as it may also indicate other serious conditions that require prompt medical attention, such as kidney stones or bladder cancer.
5. General Fatigue or Malaise
In some cases, a UTI can lead to systemic symptoms, including fatigue, malaise, or a general feeling of being unwell. These symptoms may arise when the infection spreads to the kidneys, causing a more severe condition known as pyelonephritis or kidney infection. In such instances, the body's immune response to the infection can result in overall weakness, fatigue, and a sense of unwellness. For example, a person may experience persistent tiredness, body aches, and a lack of energy. If you have these symptoms, especially alongside other UTI symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical care promptly to prevent complications.
While the presence of one or more of these signs does not guarantee a urinary tract infection diagnosis, it is crucial to be able to recognize the symptoms of a potential infection. UTIs are common and can occur in individuals of all ages, so it is important to listen to your body and consult a healthcare professional if you experience any concerning symptoms. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage UTIs and maintain optimal urinary tract health.



